Abstract
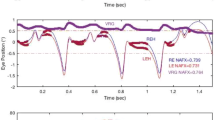
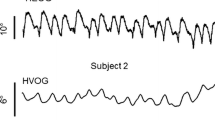
It has been shown that, during fixation of a stationary target with a fixed head, an individual with congenital nystagmus (CN) can repeatedly (beat-to-beat) foveate (within 13 minarc) and maintain low retinal slip velocities (less than 4°/sec). With the head in motion, vestibuloocular reflex (VOR) data showed eye velocities during these foveation periods that approximation head veloicty. Despite some claims that the VOR of CN subjects was deficient or absent, individuals with CN hardly ever complain of oscillopsia or exhibit any of the symptoms that would accompany such deficits in the VOR, whether during simple walking and running or while skiing down a mogul field. We developed and describe several different and unrelated methods to accurately assess the function of the VOR in an individual with typical idiopathic CN. We investigated the dynamics of CN foveation periods during head rotation to test the hypothesis that eye velocities would match head velocities during these periods. At about 1 Hz, horizontal VOR instantaneous (beat-to-beat) gains were 0.96 in the light and 0.94 in the dark while imagining a stationary target. Vertical VOR gains were 1.00 and 0.99 for these two conditions at the same frequency; the CN was horizontal. Also, during the VOR there is a CN neutral-zone shift comparable to that found during smooth pursuit. Our methods demonstrated that gaze velocity was held constant during foveation periods and we conclude that the VOR in this subject is functioning normally in the presence of the CN oscillation. Based on our findings in this and previous studies, we hypothesize that CN may be due to a peripheral instability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BS:
-
Braking saccade
- CN:
-
Congenital nystagmus
- CS:
-
Catch-up saccade
- DNZ:
-
Dynamic neutral zone
- FS:
-
Foveating saccade
- NFP:
-
Non-foveating peak
- SNZ:
-
Static neutral zone
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- VOR:
-
Vestibulo-ocular reflex
- JLef:
-
Jerk left with extended foveation
- Pfr(l)s:
-
Pendular with right (left) foveating saccades
- PPr(l)fs:
-
Pseudopendular with right (left) foveating saccades
- R(L)PC:
-
Right (left) pseudocycloid
- Gav:
-
Average gain
- Gfp:
-
Gain calculated during the foveation period
- RERfp:
-
Mean retinal error position during foveation period
References
Dell'Osso LF. Fixation characteristics in hereditary congenital nystagmus. Am J Optom Arch AM Acad Optom 1973; 50: 85–90.
Dell'Osso LF, Daroff RB. Congenital nystagmus waveforms and foveation strategy. Doc Ophthalmol 1975; 39: 155–182.
Gresty MA, Barratt HJ, Page NG, Ell JJ. Assessment of vestibulo-ocular reflexes in congenital nystagmus. Ann Neurol 1985; 17: 129–136.
Dell'Osso LF. Evaluation of smooth pursuit in the presence of congenital nystagmus. Neuro-ophthalmol 1986; 6: 383–406.
Kurzan R, Büttner U. Smooth pursuit mechanisms in congenital nystagmus. Neuro-ophthalmol 1989; 9: 313–325.
Collewijn H, Van Der Mark F, Jansen TC. Precise recordings of human eye movements. Vision Res 1975; 15: 447–450.
Steinman RM, Collewijn H. Binocular retinal image motion during active head rotation. Vision Res 1980; 20: 415–429.
Collewijn H, Erkelens CJ, Steinman RM. Binocular co-ordination of human horizontal saccadic eye movements. J Physiol 1988; 404: 157–182.
Collewijn H, Erkelens CJ, Steinman RM. Binocular co-ordination of human vertical saccadic eye movements. J Physiol 1988; 404: 183–197.
Dell'Osso LF, Van der Steen J, Steinman RM, Collewijn H. Foveation dynamics in congenital nystagmus, I: Fixation. Doc Ophthalmol 1992; 79: 1–23.
Dell'Osso LF, Van der Steen J, Steinman RM, Collewijn H. Foveation dynamics in congenital nystagmus, II: Smooth pursuit. Doc Ophthalmol 1992; 79: 25–49.
Papoulis A. Signal Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1977: 234–239.
Hary D, Oshio K, Flanagan SD. The ASYST software for scientific computing. Science 1987; 236: 1128–1132.
Daroff RB, Dell'Osso LF. Periodic alternating nystagmus and the shifting null. Can J Otolaryngol 1974; 3: 367–371.
Furman JM, Stoyanoff S, Barber HO. Head and eye movements in congenital nystagmus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1984; 92: 656–661.
Demer JL, Zee DS. Vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic defects in albinos with congenital nystagmus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1984; 25: 739–745.
Carl JR, Optican LM, Chu FC, Zee DS. Head shaking and vestibulo-ocular reflex in congenital nystagmus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1985; 26: 1043–1050.
Gresty MA, Halmagyi GM, Leech J. The relationship between head and eye movement in congenital nystagmus with head shaking: objective recordings of a single case. Br J Ophthalmol 1978; 62: 533–535.
Yee RD, Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Kim YS. A study of congenital nystagmus: vestibular nystagmus J Otolaryngol 1981; 10: 89–98.
Dell'Osso LF, Traccis S, Abel LA, Erzurum SI. Contact lenses and congenital nystagmus. Clin Vision Sci 1988; 3: 229–232.
Dell'Osso LF, Leigh RJ, Daroff RB. Suppression of congenital nystagmus by cutaneous stimulation. Neuro-ophthalmol 1991; 11: 173–175.
Dell'Osso LF, Flynn, JT. Congenital nystagmus surgery: a quantitative evaluation of the effects. Arch Ophthalmol 1979; 97: 462–469.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dell'Osso, L.F., Van Der Steen, J., Steinman, R.M. et al. Foveation dynamics in congenital nystagmus III: Vestibulo-ocular reflex. Doc Ophthalmol 79, 51–70 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160132
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160132