Summary
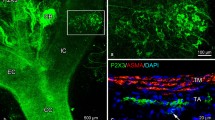
Immunohistochemical localization of substance P (SP), CGRP, VIP, neuropeptide Y (NPY), and somatostatin (SOM) in the carotid labyrinth were compared in some species of amphibians using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. Immunoreactivity of SP, CGRP, VIP, and NPY was found in the nerve fibers distributed in the intervascular stroma of the carotid labyrinth. SP, CGRP, and VIP immunoreactive varicose fibers were densely distributed in the peripheral portion of the carotid labyrinth. Some SP-immunoreactive fibers were distributed similarly to CGRP-immunoreactive fibers. The density of NPY and SOM immunoreactive varicose fibers was low. No immunoreactivity of enkephalins was observed in the labyrinth. The intensities of these peptides were varied from species to species. No glomus cells showed immunoreactivity for any of the 7 peptides studied. These results suggest that the vascular regulatory function, which is one of the possible functions of the carotid labyrinth, is controlled by the peptidergic mechanisms in addition to regulation through intimate apposition of glomus and smooth muscle cells (g-s connection).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WE (1958) The comparative morphology of the carotid body and carotid sinus. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, pp 202–214
Anglade P, Tsuji S (1990a) Simultaneous localization of neuropeptides (Substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) with acetylcholine-like cation at electron microscopic level. Acta Histochem Cytochem 23:219–226
Anglade P, Tsuji S (1990b) Ultrastructural simultaneous localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide immunoreactivity and the acetylcholine-like cation in rat endocrine pancreas. Arch Histol Cytol 53:553–558
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Moris HR, MacIntyre (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Cuello AC, McQueen DS (1980) Substance P: a carotid body peptide. Neurosci Lett 17:215–219
Edvinsson L, McCulloch J, Uddman R (1981) Substance P: immunohistochemical localization and effect upon feline pial arteries in vitro and in situ. J Physiol (Lond) 318:251–258
Edvinsson L, Uddman R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization and dilatatory effect of substance P on human cerebral vessels. Brain Res 232:466–471
Edvinsson L, Emson P, McCulloch J, Teramoto K, Uddman R (1983) Neuropeptide Y: cerebrovascular innervation and vasomotor effects in the cat. Neurosci Lett 43:79–84
Graham RC, Karnovsky MJ (1966) The early stage of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Hallberg D, Pernow B (1975) Effect of substance P on various vascular beds in the dog. Acta Physiol Scand 93:277–285
Hansen JT, Grokaw J, Christie D, Karasek M (1982) Localization of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the cat carotid and aortic body chemoreceptors. Anat Rec 203:405–410
Ishii K, Ishii K (1973) Fiber composition and derivation of afferent and efferent nerve fibers in the carotid nerve innervating the carotid labyrinth of the toad. Tohoku J Exp Med 109:323–337
Ishii K, Oosaki T (1969) Fine structure of the chemoreceptor cell in the amphibian carotid labyrinth. J Anat 104:263–280
Ishii K, Kusakabe T (1982) The glomus cell of the carotid labyrinth of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res 224:459–463
Ishii K, Honda K, Ishii K (1966) The function of the carotid labyrinth in the toad. Tohoku J Exp Med 88:103–116
Jacobowitz DM, Helke CJ (1980) Localization of substance P immunoreactive nerves in the carotid body. Brain Res Bull 5:195–197
Kameda Y (1989) Distribution of CGRP-, somatostatin-, galanin-, VIP-, and substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the chicken carotid body. Cell Tissue Res 257:623–629
Kobayashi S (1971) Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. 1. Demonstration of monoamine-storing cells by correlated chromaffin reaction and fluorescence histochemistry. Arch Histol Jpn 33:319–339
Kobayashi S (1971) Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. 2. Ultrastructure of the synapse on the chief cell. Arch Histol Jpn 33:397–420
Kobayashi S, Uchida T, Ohashi T, Fujita T, Nakao K, Yoshimasa T, Imura H, Mochizuki T, Yanaihara C, Yanaihara N, Verhofstad AAJ (1983) Immunocytochemical demonstration of the co-storage of noradrenaline with met-enkephalin-arg6-phe7 and met-enlephalin-arg6-gly7-leu8 in the carotid body chief cells of the dog. Arch Histol Jpn 46:713–722
Kondo H, Kuramoto H, Fujita T (1986) Neuropeptide tyrosine-like immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid body chemoreceptor of rats. Brain Res 372:353–356
Kusakabe T (1990a) Ultrastructural studies of the carotid labyrinth in the newt Cynops pyrrhogaster. Zool Sci 7:201–208
Kusakabe T (1990b) Comparative studies on the vascular organization of carotid labyrinths of anurans and caudates. J Morphol 204:47–55
Kusakabe T, Ishii K, Ishii K (1987) A possible role of the glomus cell in controlling vascular tone of the carotid labyrinth of Xenopus laevis. Tohoku J Exp Med 151:395–408
Larsson LI, Edvinsson L, Fahrenkrug R, Hakanson R, Owman CH, Schaffalitzky O de Muckadell, Sundler F (1976) Immunohistochemical localization of a vasodilatory polypeptide (VIP) in cerebrovascular nerves. Brain Res 113:400–404
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Fahrenkrug J, Nilsson G, Terenius L (1979a) Peptides in the carotid body (glomus caroticum): VIP-, enkephalin- and substance P-like immunoreactivity. Acta Physiol Scand 107:279–281
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Schultzberg M, Uvnas-Wallenstein K, Kohler C, Said SI (1979b) Occurrence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-like immunoreactivity in certain cholinergic neurons of the cat: evidence from combined immunohistochemistry and acctylcholinesterase staining. Neuroscience 4:1539–1559
Lundberg JM, Anggard A, Fahrenkrug J, Hökfelt T, Mutt V (1980) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cholinergic neurons of exocrine glands: functional significance of coexisting transmitters for vasodilation and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1651–1655
Lundberg JM, Terenis L, Hökfelt T, Martling CR, Tatemoto K, Mutt V, Polak J, Bloom S, Goldstein M (1982) Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand 116:477–480
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T (1983) Coexistence of peptides and classical neurotransmitters. Trends Neurosci 6:325–333
Matsuyama T, Shiosaka S, Matsumoto M, Yoneda S, Kimura K, Abe H, Hayakawa T, Inoue H, Tohyama M (1983) Overall distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing nerves on the wall of cerebral arteries: an immunohistochemical study using whole-mounts. Neuroscience 10:89–96
Matsuyama T, Shiosaka S, Wanaka A, Yoneda S, Kimura K, Hayakawa T, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Fine structure of peptidergic and catecholaminergic nerve fibers in the cerebral artery and their interrelationship: an immunoelectromicroscopic study. J Comp Neurol 235:268–276
Rogers DC (1963) Distinct cell types in the carotid labyrinth. Nature 200:492–493
Samnegård H, Thulin L, Tydén G, Johansson C, Muhrberg O, Björklund C (1978) Effect of synthetic substance P on internal carotid artery blood flow in man. Acta Physiol Scand 104:492–495
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Smith P, Gosney J, Heath D, Burnet H (1990) The occurrence and distribution of certain polypeptides within the human carotid body. Cell Tissue Res 261:565–571
Varndell IM, Tapia FJ, Mey JD, Rush RA, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1982) Electron immunocytochemical localization of enkephalin-like material in catecholamine-containing cells of the carotid body, the adrenal medulla, and in pheochromocytomas of man and other mammals. J Histochem Cytochem 30:682–690
Wanaka A, Matsuyama T, Yoneda S, Kimura K, Kamada T, Girgis S, McIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1986) Origins and distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing nerves in the wall of the cerebral arteries of the guinea pig with special reference to the coexistence with substance P. Brain Res 369:185–192
Wharton J, Polak JM, Pearse AGE, McGregor GP, Bryant MG, Bloom SR, Emson PC, Bisgard GE, Will JA (1980) Enkephalin-, VIP- and substance P-like immunoreactivity in the carotid body. Nature 284:269–271
Yamauchi A (1977) On the recepto-endocrine property of granule-containing (GC) cells in the autonomic nervous system. Arch Histol Jpn 40 [Suppl]:147–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusakabe, T., Anglade, P. & Tsuji, S. Localization of substance P, CGRP, VIP, neuropeptide Y, and somatostatin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinths of some amphibian species. Histochemistry 96, 255–260 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271544
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271544