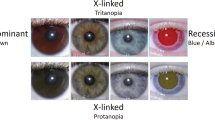
Abstract
Paired box (PAX) genes play a critical role in human development and disease. The PAX2 gene is expressed in primitive cells of the kidney, ureter, eye, ear and central nervous system. We have conducted a mutational analysis of PAX2 in a family with optic nerve colobomas, renal hypoplasia, mild proteinuria and vesicoureteral reflux. We report a single nucleotide deletion in exon five, causing a frame–shift of the PAX2 coding region in the octapeptide domain. The phenotype resulting from the PAX2 mutation in this family was very similar to abnormalities that have been reported in Krd mutant mice. These data suggest that PAX2 is required for normal kidney and eye development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weaver, R.G. et al. Optic nerve coloboma associated with renal disease. Am. J. mad. Genet. 29, 597–605 (1988).
Antignac, C. et al. A gene for familial juvenile nephronophthisis (recessive medullary cystic kidney disease) maps to chromosome 2p. Nature Genet. 3, 342–345 (1993).
Clarke, M.P. et al. Senior-Loken syndrome. Case report of two siblings and association with sensorlneural deafness. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 76, 171–172 (1992).
Mann, I. The development of the human eye. 1–29 (Grune and Stratton, New York, 1928).
Saxen, L. Organogenesis of the kidney. 1–34 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987).
Dressier, G.R., Deutsch, U., Chowdhury, K., Nornes, H.O. & Gruss, P. Pax2, a new murine paired-box-containing gene and its expression in the developing excretory system. Development. 109, 787–795 (1990).
Nornes, H.O., Dressier, G.R., Knapik, E.W., Deutsch, U. & Gruss, P. Spatially and temporally restricted expression of Pax2 during murine neurogenesis. Development 109, 797–809 (1990).
Treisman, J., Harris, E. & Desplan, C. The paired box encodes a second DNA-binding domain in the paired homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 5, 594–604 (1991).
Gruss, P. & Walther, C. Pax in development. Cell 69, 719–722 (1992).
Tassabehji, M. et al. Waardenburgs syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature 355, 635–636 (1992).
Baldwin, C.T., Hoth, C.F., Amos, J.A., da-Silva, E.O. & Milunsky, A. An exonic mutation in the HuP2 paired domain gene causes Waardenburgs syndrome. Nature 355, 637–638 (1992).
Jordan, T. et al. The human PAX6 gene is mutated in two patients with aniridia. Nature Genet. 1, 328–332 (1992).
Ton, C.C.T. et al. Positional cloning and characterization of a paired box-and homeobox-containing gene from the aniridia region. Cell. 67, 1059–1074 (1991).
Glaser, T., Walton, D.S. & Maas, R.L. Genomic structure, evolutionary conservation and aniridia mutations in the human PAX6 gene. Nature.Genet. 2, 232–238 (1992).
Barr, F.G. et al. Rearrangement of the PAX3 paired box gene in the paediatric solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nature Genet. 3, 113–117 (1993).
Eccles, M.R. et al. Expression of the PAX2 gene in human fetal kidney and Wilms Tumor. Cell Growth Diff. 3, 279–289 (1992).
Stapleton, P., Weith, A., Urbanek, P., Kozmik, Z. & Busslinger, M. Chromosomal localization of seven PAX genes and cloning of a novel family member, PAX-9. Nature Genet. 3, 292–298 (1993).
Dressier, G.R. et al. Deregulation of Pax-2 expression in transgenic mice generates severe kidney abnormalities. Nature 362, 65–67 (1993).
Rothenpieler, U.W. & Dressier, G.R. Pax-2is required for mesenchyme-to-epithelium conversion during kidney development. Development 119, 711–720 (1993).
Keller, S.A. et al. Kidney and retinal defects (Krd), a transgene induced mutation with a deletion of mouse chromosome 19 that includes the Pax-2 locus. Genomics 23, 309–320 (1994).
Fisher, E. & Scambler, P. Human haploinsufficiency — one for sorrow, two for joy. Nature Genet. 7, 5–7 (1994).
Ward, T.A., Nebel, A., Reeve, A.E. & Eccles, M.R. Alternative messenger RNA forms and open reading frames within an additional conserved region of the human PAX-2 gene. Cell Growth Diff. 5, 1015–1021 (1994).
Kozmik, Z., Kurzbauer, R., Dorfler, P. & Busslinger, M. Alternative splicing of Pax-8 gene transcripts is developmentally regulated and generates isoforms with different transactivation properties. Molec. cell. Blol. 13, 6024–6035 (1993).
Eccles, M.R., Yun, K., Reeve, A.E & Fldler, A.E. Comparative In situ Hybridization analysis of PAX2, PAX8, and WT1 gene transcription in human fetal kidney and Wilms tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 40–45 (1995).
Plachov, D. et al. Pax8, a murine paired box gene expressed in the developing excretory system and thyroid gland. Development 110, 643–651 (1990).
Pierpont, J.W. & Erickson, R.P. Facts on PAX. Am. J. hum. Genet. 52, 451–454 (1993).
Püschel, A.W., Wests-field, M. & Dressier, G.R. Comparative analysis of Pax-2 protein distributions during neurulation in mice and zebrafish. Mech. Devel. 38, 197–208 (1992).
Phelps, D.E. & Dressier, G.R. Aberrant expression of Pax-2 in Danforths Short Tail (Sd) Mice. Dev. Biol., 157, 251–258 (1993).
Balling, R., Deutsch, U. & Gruss, P. Undulated, a mutation affecting the development of the mouse skeleton, has a point mutation in the paired box of Pax 1. Cell 55, 531–535 (1988).
Epstein, D.J., Vekemans, M. & Gross, P. splotch. (SP2H), a mutation affecting development of the mouse neural tube, shows a deletion within the paired homeodomain of Pax-3. Cell 67, 767–774 (1991).
Hill, R.E. et al. Mouse Small eye results from mutations in a paired-tike homeobox-containing gene. Nature 354, 522–525 (1991).
Cohen, J., Burne, J.F., McKinlay, C. & Winter, J. The role of laminin and the laminin/fibronectin receptor complex in the outgrowth of retinal ganglion cell axons. Dev. Biol. 122, 407–418 (1987).
Chalepakis, G., Goulding, M., Read, A., Strachan, T. & Gruss, P. Molecular basis of Splotch and Waardenburg Pax-3 mutations. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 3685–3689 (1994).
Tassabehji, M. et al. Mutations in the PAX3 gene causing Waardenburg syndrome type 1 and type 2. Nature Genet. 3, 26–30 (1992).
Hanson, I.M. et al. PAX6mutations in aniridia. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 915–920 (1993).
Davis, A. & Cowell, J.K. Mutations in the PAX6 gene in patients with hereditary aniridia. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 2093–2097 (1993).
Pagon, R.A., Graham, J.M. Jr. & Zonana, J., Yong, S.-L. Coloboma, congenital heart disease, and choanal atresia with multiple anomalies: CHARGE association. J. Pediat. 99, 223–227 (1981).
Leppert, M. et al. Bardet-Biedl syndrome is linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11q and is genetically heterogeneous. Nature Genet. 7, 108–112 (1994).
Reiger, G. Zum Krankheitsbild der Handmannschen Sehnervenanomalie: Windenbluten-(Morning Glory) Syndrom? Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 170, 697–706 (1977).
Karcher, H. Zum Morning glory syndrome. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 175, 835–840 (1979).
Legros, Y., Carrenard, J.R., Cortes, F.M., Sanchez, J.M. Sindrome de “ojo de gato” con agenesia renal derecha. Aportacion de un caso y revision de la literatura. An. Esp. Pediatr. 36, 317–319 (1992).
Bron, A.J., Burgess, S.E., Awdry, P.N., Oliver, D., Arden & G. Papillo-renal syndrome. An inherited association of optic disc dysplasia and renal disease. Report and review of the literature. Ophthalmic Paediatr. Genet. 10, 185–198 (1989).
Pagon, R.A. Ocular coloboma. Surv. Ophth. 25, 223–236 (1981).
Grossberger, D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 6737 (1987).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. 2nd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Orita, M., Suzuki, Y., Sekiya, T. & Hayashi, K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5, 874–879 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanyanusin, P., Schimmenti, L., McNoe, L. et al. Mutation of the PAX2 gene in a family with optic nerve colobomas, renal anomalies and vesicoureteral reflux. Nat Genet 9, 358–364 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0495-358
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0495-358
This article is cited by
-
Ocular manifestations of renal ciliopathies
Pediatric Nephrology (2024)
-
Lactate-dependent transcriptional regulation controls mammalian eye morphogenesis
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Effects of the environment on the evolution of the vertebrate urinary tract
Nature Reviews Urology (2023)
-
The genetic basis of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract
Pediatric Nephrology (2022)