Abstract
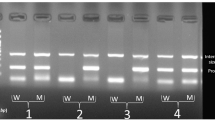
The aim of this study was to investigate the association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in IL23R with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in Chinese Han population. Six SNPs were selected for analysis in AS patients and controls. The IL23R mRNA expression was detected using RT-PCR. The differences in the genotypes of rs11209032 and the differences in the genotypes and allele frequencies of rs6677188 between cases and controls were significant. The two SNPs rs11209032 and rs6677188 were in strong linkage disequilibrium. Haplotype analysis noted a higher proportion of GAC in cases and a higher proportion of GTC in controls. The patients with AS showed an elevated level of IL23R mRNA in PBMCs. This study suggested that IL23R polymorphisms were associated with susceptibility to AS in the Chinese population and that IL23R may be involved in the development of AS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown MA, Kennedy LG, MacGregor AJ, Darke C, Duncan E, Shatford JL et al (1997) Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: the role of genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheum 40:1823–1828. doi:10.1002/art.1780401015
Timms AE, Crane AM, Sims AM, Cordell HJ, Bradbury LA, Abbott A et al (2004) The interleukin 1 gene cluster contains a major susceptibility locus for ankylosing spondylitis. Am J Hum Genet 75:587–595. doi:10.1086/424695
Brown MA, Edwards S, Hoyle E, Campbell S, Laval S, Daly AK et al (2000) Polymorphisms of the CYP2D6 gene increase susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Hum Mol Genet 9:1563–1566. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.11.1563
Tsui FW, Tsui HW, Cheng EY, Stone M, Payne U, Reveille JD et al (2003) Novel genetic markers in the 5′-flanking region of ANKH are associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 48:791–797. doi:10.1002/art.10844
Trinchieri G, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA (2003) The IL-12 family of heterodimeric cytokines: new players in the regulation of T-cell responses. Immunity 19:641–644. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00296-6
Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, Vaisberg E, Travis M, Cheung J et al (2002) A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rβ1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol 168:5699–5708
Belladonna ML, Renauld JC, Bianchi R, Vacca C, Fallarino F, Orabona C et al (2002) IL-23 and IL-12 have overlapping, but distinct effects on murine dendritic cells. J Immunol 168:5448–5454
Zhang XY, Zhang HJ, Zhang Y, Fu YJ, He J, Zhu LP et al (2006) Identification and expression analysis of alternatively spliced isoforms of human interleukin-23 receptor gene in normal lymphoid cells and selected tumor cells. Immunogenetics 57:934–943. doi:10.1007/s00251-005-0067-0
Tremelling M, Cummings F, Fisher SA, Mansfield J, Gwilliam R, Keniry A et al (2007) IL23R variation determines susceptibility but not disease phenotype in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 132:1657–1664. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.02.051
Capon F, Di Meglio P, Szaub J, Prescott NJ, Dunster C, Baumber L et al (2007) Sequence variants in the genes for the interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R) and its ligand (IL12B) confer protection against psoriasis. Hum Genet 122:201–206. doi:10.1007/s00439-007-0397-0
Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M, Garcia VE, Brandon R, Callis KP et al (2007) A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 80:273–290. doi:10.1086/511051
Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, Craddock N, Deloukas P, Duncanson A et al (2007) Association scan of 14500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 39:1329–1337. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.17
Hunter CA (2005) New IL-12-family members: IL-23 and IL-27, cytokines with divergent functions. Nat Rev Immunol 5:521–531. doi:10.1038/nri1648
McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2006) Understanding the IL-23-IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol 27:17–23. doi:10.1016/j.it.2005.10.003
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL, Pittman D, Wang F, Chamian F et al (2004) Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med 199:125–130. doi:10.1084/jem.20030451
Schmidt C, Giese T, Ludwig B, Mueller-Molaian I, Marth T, Zeuzem S et al (2005) Expression of interleukin-12-related cytokine transcripts in inflammatory bowel disease: elevated interleukin-23p19 and interleukin-p27p28 in Crohn’s disease but not in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11:16–23. doi:10.1097/00054725-200501000-00003
Ware CF (2005) Network communications: lymphotoxins, LIGHT, and TNF. Annu Rev Immunol 23:787–819. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115719
Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, Rioux JD, Silverberg MS, Daly MJ et al (2006) A genome-wide association study identifies IL-23R as an inflammatory disease gene. Science 314:1461–1463. doi:10.1126/science.1135245
Van Limbergen J, Russell RK, Nimmo ER, Drummond HE, Smith L, Davies G et al (2007) IL23R Arg381Gln is associated with childhood onset inflammatory bowel disease in Scotland. Gut 56:1173–1174. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.122069
Libioulle C, Louis E, Hansoul S, Sandor C, Farnir F, Franchimont D et al (2007) Novel Crohn disease locus identified by genome-wide association maps to a gene desert on 5p13.1 and modulates expression of PTGER4. PLoS Genet 20:e58. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030058
Oliver J, Rueda B, López-Nevot MA, Gomez-Garcia M, Martin J (2007) Replication of an association between IL23R gene polymorphism with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:977–981. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.05.002
Orozco G, Rueda B, Robledo G, García A, Martín J (2007) Investigation of the IL23R gene in a Spanish rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Hum Immunol 68:681–684. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2007.05.008
Sanchez E, Rueda B, Callejas JL, Sabio JM, Ortego-Centeno N, Jimenez-Alonso J et al (2007) Analysis of interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R) gene polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens 70:233–237. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2007.00881.x
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the participants who contributed their blood samples to our study. Dr. Gu’s work was funded by Research Grant 30325019 of National Science in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Huang, J., Lin, Z. et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and expression of IL23R in Chinese ankylosing spondylitis patients. Rheumatol Int 30, 955–959 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1085-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1085-2