Summary
Background: Applanation tonometry in eyes with pathological corneae can often not be performed or delivers rather questionable results. We report on our 4-year experience with electronic intraocular needle tonometry.
Patients and methods: After since 1994 developing and calibrating a system for intraocular needle tonometry, we have performed 395 measurements in 252 eyes with irregular corneae and suspicion of glaucoma. If applanation tonometry values could be obtained, they were compared with the true intraocular pressure.
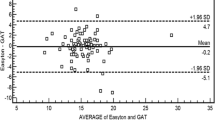
Results: Depending on the kind of corneal pathology, applanation tonometry values were lower and sometimes much lower than true intraocular pressure. No serious complications occurred as a result of intraocular needle tonometry.
Conclusions: Intraocular needle tonometry is a safe procedure and is the only way to measure intraocular pressure precisely in eyes with pathological corneae.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund: Die Augeninnendruckmessung mittels Applanation an pathologisch veränderten Hornhäuten ist oft nicht möglich oder ihre Ergebnisse sind äußerst zweifelhaft. Wir berichten über unsere mehr als vierjährige Erfahrung mit der elektronischen intraokularen Nadel-Druckmessung bei irregulären Hornhäuten.
Patienten und Methode: Nach Entwicklung und Eichung des intraokularen Nadel-Druckmessverfahrens wurden seit 1994 an 252 Augen mit irregulären Hornhäuten und Glaukomverdacht 395 Messungen durchgeführt. Die Ergebnisse der intraokularen Messungen wurden mit den nur bei einem Teil der Patienten applanatorisch ermittelbaren Werten verglichen.
Ergebnisse: Die applanatorisch erhobenen Werte lagen meist tiefer und je nach Hornhautpathologie manchmal sehr viel tiefer als die tatsächlichen intraokularen Werte. Ernsthafte Komplikationen der intraokularen Messung wurden bisher nicht beobachtet.
Schlußfolgerung: Die intraokulare Druckmessung ist sicher und ermöglicht die exakte Ermittlung des intraokularen Druckes auch in Augen mit pathologisch veränderten Hornhäuten.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marx, W., Madjlessi, F., Reinhard, T. et al. More than 4 years' experience with electronic intraocular needle tonometry. Ophthalmologe 96, 498–502 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050444
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050444