Abstract
Purpose
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) is one of the most potent lymphangiogenic members of the VEGF family that has been associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). In this study, we evaluated the relationship of preoperative serum VEGF-C (sVEGF-C) and survival in CRC patients.
Materials and methods
sVEGF-C levels were determined, prior to resection, in a cohort of 120 newly presenting patients with CRC by quantitative ELISA.
Results
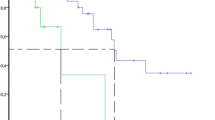
Patients who had positive lymph node involvement and higher Dukes’ staging (C&D) were associated with shorter time to metastases as expected (p = 0.002 and 0.001, respectively). Patients with distant metastasis had significantly lower levels of sVEGF-C than those without histopathologically proven disease (p = 0.004). However, there was no significant difference in the median sVEGF-C level in patients with or without lymph node metastatic involvement (91 pg/ml vs. 124 pg/ml; p = 0.81). Patients with a sVEGF-C concentration less than the median value (103 pg/ml) showed a poorer overall survival than patients with sVEGF-C levels greater than the median; but this was not statistically significant.
Conclusions
In this study, low sVEGF-C levels are associated with distant metastasis; hence, preoperative levels may aid in the selection of CRC patients who require further investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
UK, C.R., Large Bowel (Colorectal) Cancer Factsheet April 2005.
Globocan, International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2002
UICC, TNM classification of malignant tumours. 2002 (6th Ed)
Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Mamon HJ et al (2007) Adjuvant treatment of colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 57:168–185
Giuliani F, Colucci G (2007) Cetuximab in colon cancer. Int J Biol Markers 22:S62–S70
Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS et al (1995) Fluorouracil plus levamisole as effective adjuvant therapy after resection of stage III colon carcinoma: a final report. Ann Intern Med 122(5):321–326
O’Dwyer ST, Haboubi NY, Johnson JS et al (2001) Detection of lymph node metastases in colorectal carcinoma. Colorectal Dis 3:288–294
Pepper MS (2001) Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis: myth or reality? Clin Cancer Res 7:462–468
George ML, Tutton MG, Janssen F et al (2001) VEGF-A, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D in colorectal cancer progression. Neoplasia 3:420–427
Stacker SA, Achen MG, Jussila L et al (2002) Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2:573–583
Jeltsch M, Kaipainen A, Joukov V et al (1997) Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science 276:1423–1425
Kukk E, Lymboussaki A, Taira S et al (1996) VEGF-C receptor binding and pattern of expression with VEGFR-3 suggests a role in lymphatic vascular development. Development 122:3829–3837
Joukov V, Sorsa T Kumar V et al (1997) Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity of VEGF-C. Embo J 16:3898–3911
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A et al (1996) A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. Embo J 15:1751
Paavonen K, Horelli-Kuitunen N, Chilov D et al (1996) Novel human vascular endothelial growth factor genes VEGF-B and VEGF-C localize to chromosomes 11q13 and 4q34, respectively. Circulation 93:1079–1082
Mohammed RA, Green A, El-Shikh S et al (2007) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors -A, -C and -D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio- and lymphangiogenesis. Br J Cancer 96:1092–1100
Yonemura Y, Fushida S, Bando E et al (2001) Lymphangiogenesis and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-3 in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 37:918–923
Nishida N, Yano H, Komai K et al (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor C and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 are related closely to the prognosis of patients with ovarian carcinoma. Cancer 101:1364–1374
Furudoi A, Tanaka S, Haruma K et al (2002) Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor C expression and angiogenesis at the deepest invasive site of advanced colorectal carcinoma. Oncology 62:157–166
Rubbia-Brandt L, Terris B, Giostra E et al (2004) Lymphatic vessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression correlate with malignant behavior in human pancreatic endocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10:6919–6928
Liotta LA (1986) Tumor invasion and metastases—role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res 46:1–7
Yang W, Klos K, Yang Y et al (2002) ErbB2 overexpression correlates with increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, C, and D in human breast carcinoma. Cancer 94:2855–2861
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. Embo J 20:672–682
Duff SE, Saunders M, McCredie V et al (2005) Pre-operative plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A, C and D in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 17:367–371
Akagi K, Ikeda Y, Miyazaki M et al (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) expression in human colorectal cancer tissues. Br J Cancer 83:887–891
Hu WG, Li JW, Feng B et al (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factors C and D represent novel prognostic markers in colorectal carcinoma using quantitative image analysis. Eur Surg Res 39:229–238
Noda E, Maeda K, Inoue T et al (2007) Predictive value of vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression for local recurrence of rectal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 17:1327–1331
Onogawa S, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S et al (2004) Expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D at the invasive edge correlates with lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 95:32–39
Xu T, Chen D (2006) Serum vascular endothelial growth factor-C and Vascular endothelial growth factor level in patients with colorectal carcinoma and clinical significance. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Med Sci] 26:329–331
Tamura M, Ohta Y (2003) Serum vascular endothelial growth factor-C level in patients with primary nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: a possible diagnostic tool for lymph node metastasis. Cancer 98:1217–1222
Kinoshita J, Kitamura K, Kabashima A et al (2001) Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 66:159–164
Wartiovaara U, Salven P, Mikkola H et al (1998) Peripheral blood platelets express VEGF-C and VEGF which are released during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 80:171–175
Hyodo I, Doi T, Endo H et al (1998) Clinical significance of plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in gastrointestinal cancer. Eur J Cancer 34:2041–2045
Dirix LY, Vermeulen PB, Hubens G et al (1996) Serum basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor and tumour growth kinetics in advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 7:843–848
Lee JC, Chow NH, Wang SM, Huang SM (2000) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colorectal cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 36:748–753
Nissen NN, Polverini PJ, Koch AE et al (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates angiogenic activity during the proliferative phase of wound healing. Am J Pathol 152:1445–1452
George ML, Eccles SA, Tutton MG et al (2000) Correlation of plasma and serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels with platelet count in colorectal cancer: clinical evidence of platelet scavenging? Clin Cancer Res 6:3147–3152
Werther K, Christensen IJ, Nielsen HJ (2002) Prognostic impact of matched preoperative plasma and serum VEGF in patients with primary colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 8:417–423
Acknowledgements
We thank Rachel Waddington of ANR statistical consultants for advice on statistical analysis and acknowledge the assistance of members of the Academic Surgical Unit for patient recruitment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alabi, A.A., Suppiah, A., Madden, L.A. et al. Preoperative serum levels of serum VEGF-C is associated with distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis 24, 269–274 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-0622-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-0622-x