Abstract
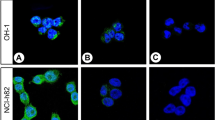
Although it is widely accepted that specific intracellular receptor proteins are involved in the oestrogenic regulation of gene expression and growth in reproductive tissues, the precise nature of the regulation is poorly understood. Among the unresolved issues are the distribution and dynamics of the oestrogen receptor protein (oestrophilin) in target tissues in the presence and absence of oestrogens and antioestrogens. The use of radio-labelled and unlabelled receptor ligands to detect and measure oestrogen receptors in tissues has been complicated by the presence of other intracellular steroid-binding proteins1 and by the low concentration of receptors in responsive tissues. We report here the development of an immunocytochemical procedure that is suitable for localizing oestrophilin directly in frozen tissue sections or cells from human and several non-human sources. When monoclonal antibodies to oestrophilin were used to detect receptor in various oestrogen-sensitive tissues, specific staining was confined to the nucleus of all stained cells, suggesting that both cytosol and nuclear forms of the receptor protein may reside in the nuclear compartment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mercer, W. D. et al. Cancer Res. 41, 4644–652 (1981).
Greene, G. L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 5115–5119 (1980).
Jensen, E. V. et al. Rec. Prog. Horm. Res. 38, 1–34 (1982).
Greene, G. L. & Jensen, E. V. J. steroid Biochem. 16, 353–359 (1982).
Miller, L. S. et al. Fedn Proc. 41, Abstr. 1459 (1982).
Sternberger, P. H. et al. J. histochem. Cytochem. 18, 315–333 (1970).
Childs, G. V. J. histochem. Cytochem. 31, 168–176 (1983).
Petrusz, P. J. histochem. Cytochem. 31, 177–179 (1983).
Poulsen, H. S. et al. Cancer 48, 1791–1793 (1981).
Greene, G. L. in Biochemical Actions of Hormones Vol. 11 (ed. Litwack, G.) (Academic, New York, in the press).
Bender, E. M. et al. Endocrinology 103, 1937–1943 (1978).
Jensen, E. V. & DeSombre, E. R. Science 182, 126–134 (1973).
Gorski, J. & Gannon, F. A. Rev. Physiol. 38, 425–450 (1976).
Muldoon, T. G. Endocrine Rev. 1, 339–364 (1980).
Jensen, E. V. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 59, 632–638 (1968).
Martin, P. M. & Sheridan, P. J. J. steroid Biochem. 16, 215–229 (1982).
Lee, S. H. Am. J. clin. Path. 70, 197–203 (1978).
Pertschuk, L. P. et al. Am. J. clinin. Path. 71, 504–508 (1979).
Rao, B. R. et al. Cancer 46, 2902–2906 (1980).
Pertschuk, L. P. et al. Cancer 41, 907–911 (1978).
Nenci, I. et al. J. steroid Biochem. 7, 505–510 (1976).
Underwood, J. et al. J. clin. Path. 35, 401–406 (1982).
Raam, S. et al. Eur. J. Cancer clin. Oncol. 18, 1–12 (1982).
Katzenellenbogen, J. A. et al. J. biol Chem. 258, 3487–3495 (1983).
DeGroot, L. J. & Strausser, J. L. Endocrinology 95, 74–83 (1974).
Spindler, B. J. et al. J. biol. Chem. 250, 4113–4119 (1975).
Oppenheimer, J. H. et al. Rec. Prog. Horm. Res. 32, 529–565 (1976).
Lawson, D. E. M. & Wilson, P. W. Biochem. J. 144, 573–583 (1974).
Walters, M. R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 255, 6799–6805 (1980).
Stefani, M. et al. Nature 216, 173–174 (1967).
Greene, G. L. in Gene Regulation by Steroid Hormones II (eds Roy, A. K. & Clark, J. H.) (Springer, New York, in the press).
Sica, V. et al. Biochemistry 19, 83–88 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, W., Greene, G. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature 307, 745–747 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/307745a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/307745a0
This article is cited by
-
Impaired nuclear translocation of glucocorticoid receptors: novel findings from psoriatic epidermal keratinocytes
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.