Abstract
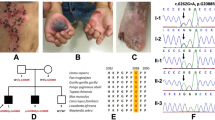
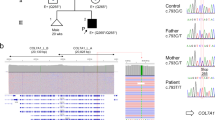
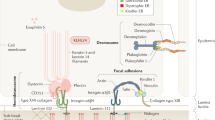
Pyloric atresia associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa (PA–JEB), is a rare inherited disorder characterized by pyloric stenosis and blistering of the skin as primary manifestations. We demonstrate that in one PA–JEB patient the disease resulted from two distinct mutations in the β4 integrin gene alleles. The paternal mutation consists of a one base pair deletion causing a shift in the open reading frame, and a downstream premature termination codon. The maternal mutation occurs in a donor splice site, and results in in–frame exon skipping involving the cytoplasmic domain of the polypeptide. Our results implicate mutations in the β4 integrin gene in some forms of PA–JEB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hynes, R.O. Integrins: versatility, modulation and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 69, 11–25 (1992).
Anderson, D.C. & Springer, T.A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: an inherited defect in the Mac-1, LFA-1, and p150,95 glycoproteins. A. Rev. Med. 38, 175–194 (1987).
George, J.N., Caen, J.P. & Nurden, A.T. Glanzmann's thrombasthenia: the spectrum of clinical disease. Blood. 75, 1383–1395 (1990).
De Luca, M. et al. Polarized integrin mediates human keratinocyte adhesion to basal lamina. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 6888–6892 (1990).
Marchisio, P.C., Bondanza, S., Cremona, O., Cancedda, R. & De Luca, M. Polarized expression of integrin receptors ( α6β4, α2β1 and αvβ5) and their relationship with the cytoskeleton and basement membrane matrix in cultured human keratinocytes. J. Cell Biol. 112, 761–773 (1991).
Larjava, H. et al. Novel function for β1 integrins in keratinocyte cell-cell interactions. J. Cell Biol. 110, 803–815 (1990).
Carter, W.G., Wayner, E.A., Bouchard, T.S. & Kaur, P. The role of integrins α2β1 and α3β1 in cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion of human epidermal cells. J. Cell Biol. 110, 1387–1404 (1990).
Carter, W.G., Kaur, P., Gil, S.G., Gahr, P.J. & Wayner, E.A. Distinct functions for integrins α3β1 in focal adhesions and α6β4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J. Cell Biol. 111, 3141–3154 (1990).
Sonnenberg, A. et al. Integrin α6β4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 113, 907–917 (1991).
Stepp, M.A., Spurr-Michaud, S., Tisdale, A., Elwell, J. & Gipson, I.K. α6β4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 8970–8974 (1990).
Jones, J.C.R., Kurpakas, M.A., Cooper, M.H. A function for the integrin α6β4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 2, 427–438 (1991).
Garrod, D.R. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 5, 30–40 (1993).
Spinardi, L., Ren, Y.-L, Sanders, R. & Giancotti, F.G. The β4 subunit cytoplasmic domain mediates the interaction of α6β4 integrin with the cytoskeleton of hemidesmosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell. 4, 871–684 (1993).
Tamura, R.N. et al. Epithelial α6β4: complete primary structure of α6 and variant forms of β4. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1593–1604 (1990).
Suzuki, S. & Naitoh, Y. Amino acid sequence of a normal integrin β4 subunit and primary expression of the mRNA in epithelial cells. EMBO J. 9, 757–763 (1990).
Hogervorst, F., Kuikman, I., Von Dem Borne, A.E. & Sonnenberg, A. Cloning and sequence analysis of β4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kD cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 9, 765–770 (1990).
Jonkman, M.F., de Jong, M.C.J.M., Heeres, K. & Sonnenberg, A. Expression of integrin α6β4 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. J. invest. Dermatol. 99, 489–496 (1992).
Phillips, R.J., Aplin, J.D. & Lake, B.D. Antigenic expression of integrin α6β4 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Histopathology. 24, 571–576 (1994).
Fine, J.D., Bauer, E.A., Briggaman, R.A. & Carter, D.M Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 24, 119–135 (1991).
Baudoin, C., Miquel, C., Blanchet-Bardon, C., Gambini, C., Meneguzzi, G. & Ortonne, J.P. Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes display heterogenous defects of nicein/kalinin gene expression. J. din. Invest. 93, 862–869 (1994).
Aberdam, D. et al. Herlitz's junctional epidermolysis bullosa is genetically linked to mutations in the nicein/kalinin (laminin 5) LAMC2 gene. Nature Genet. 6, 299–304 (1994).
Pulkkinen, L. et al. Mutations in the γ2 chain gene (LAMC2) of kalinin/laminin 5 in the junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Nature Genet. 6, 293–298 (1994).
Pulkkinen, L. et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the β3 chain gene of laminin 5 (LAMBS) in Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Genomics. 24, 357–360 (1994).
Lacour, J.P. et al. Lethal junctional epidermolysis bullosa with normal expression of BM 600 and antro-pyloric atresia: a new variant of junctional epidermolysis bullosa? Eur. J. Pediatr. 151, 252–257 (1992).
Lestringant, G.G., Akel, S.R. & Qayed, K.I. The pyloric atresia-junctional epidermolysis bullosa syndrome. Arch. Dermatol. 128, 1083–1086 (1992).
McKusick, V.A. Mendelian inheritance in man. (Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1992).
Mueller, S., Klaus-Kovtun, V. & Stanley, J.R. A 230-kD basic protein is the major bullous pemphigoid antigen. J. Invest. Dermatol. 92, 33–38 (1989).
Hieda, Y., Nishizawa, Y., Uematsu, J. & Owaribe, K. Identification of a new hemidesmosomal protein, HD1: A major, high molecular mass component of isolated hemidesmosomes. J. Cell Biol. 116, 1497–1506 (1992).
Green, M.R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 559–599 (1991).
Dietz, H.C. et al. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science 259, 680–683 (1993).
Mclntosh, I., Hamosh, A. & Dietz, H.C. Nonsense mutations and diminished mRNA levels. Nature Genet. 4, 219 (1993).
Solowska, J., Edelman, J.M., Albelda, S.M. & Buck, C.A. Cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains of integrin β1 and β2 subunits are functionally interchangeable. J. Cell Biol. 114, 1079–1088 (1991).
Pytela, R., Pierschbacher, M.D. & Ruoslahti, E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kD cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell 40, 191–196 (1985).
Benian, G.M., Kiff, J.E., Neckelmann, N., Moerman, U.G. & Waterston, R.H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature 342, 45–50 (1989).
Morla, A. & Ruoslahti, E. A fibronectin self-assembly site involved in fibronectin matrix assembly: reconstruction in a synthetic peptide. J. Cell Biol. 118, 421–429 (1992).
Giancotti, F.G., Stepp, M.A., Suzuki, S., Engvall, E. & Ruoslahti, E. Proteolytic processing of endogenous and recombinant β4 integrin subunit. J. Cell Biol. 118, 951–959 (1992).
Chang, C.H., Perrin, E.V. & Bove, K.E. Pyloric atresia associated with epidermolysis bullosa: special reference to pathogenesis. Pediatr. Pathol. 1, 449–457 (1983).
Frieden, I.J. Aplasia cutis congenita: a clinical review and proposal for for classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 14, 646–660 (1986).
Kurpakus, M.A., Quaranta, V. & Jones, J.C. Surface relocation of α6β4 integrins and assembly of hemidesmosomes in an in vitro model of wound healing. J. Cell Biol. 115, 1737–1750 (1991).
Gipson, I.K., Spurr-Michaud, S., Tisdale, A., Elwell, J. & Stepp, M.A. Redistribution of the hemidesmosome component α6β4 integrin and bullous pemphigoid antigens during epithelial wound healing. Exp. Cell Res. 207, 86–98 (1993).
Hertle, M.D., Kubler, M.D., Leigh, I.M. & Watt, F.M. Aberrant integrin expression during epidermal wound healing and in psoriatic epidermis. J. din. Invest. 89, 1892–1901 (1992).
Larjava, H., Salo, T., Haapasalmi, K., Kramer, R.H. & Heino, J. Expression of integrins and basement membrane components by wound keratinocytes. J. din. Invest. 92, 1425–1435 (1993).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY, 1989).
Ortonne, J.P. et al. The epidermal antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody GB36 is very late antigen 6 (VLA-6). J. invest. Dermatol. 94, 400 (1990).
Sonnenberg, A., Modderman, P.W. & Hogervorst, F. Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature 336, 487–489 (1988).
Kennel, S.J. et al. Second generation monoclonal antibodies to human integrin α6β4. Hybridoma 9, 243–255 (1990).
Niessen, C.M. et al. Expression of the integrin α6β4 in peripheral nerves: localization in Schwann and perineural cells and different variants of the β4 subunit. J. Cell Sci. 107, 543–552 (1994).
Tanaka, T. et al. Production of rabbit antibodies against carboxy-terminal epitopes encoded by bullous pemphigoid cDNA. J. invest Dermatol. 94, 617–623 (1989).
Owaribe, K., Nishizawa, Y. & Franke, W.W. Isolation and characterization of hemidesmosomes from bovine corneal epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 192, 622–630 (1991).
Hogervorst, F., Kuikman, I., van Kessel, G.A. & Sonnenberg, A. Molecular cloning of the human α6 integrin subunit. Alternative splicing of α6 mRNA and chromosomal localization of the α6 and β4 genes. Eur. J. Biochem. 199, 425–433 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal, F., Aberdam, D., Miquel, C. et al. Integrin β4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nat Genet 10, 229–234 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-229
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-229
This article is cited by
-
Defective perlecan-associated basement membrane regeneration and altered modulation of transforming growth factor beta in corneal fibrosis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
A novel mutation in ITGB4 gene in a newborn with epidermolysis bullosa, pyloric atresia, and aplasia cutis congenita
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2020)
-
Biologically relevant laminin as chemically defined and fully human platform for human epidermal keratinocyte culture
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Integrin-mediated regulation of epidermal wound functions
Cell and Tissue Research (2016)
-
Whole-genome sequencing identifies a homozygous deletion encompassing exons 17 to 23 of the integrin beta 4 gene in a Charolais calf with junctional epidermolysis bullosa
Genetics Selection Evolution (2015)