Abstract
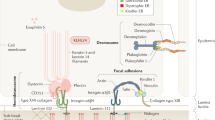
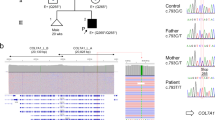
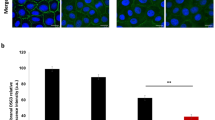
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) is a heterogeneous autosomal recessively inherited blistering skin disorder associated with fragility at the dermal-epidermal junction1. Characteristic ultrastructural findings in JEB are abnormalities in the hemidesmosome-anchoring filament complexes1,2. These focal attachment structures, which extend from the intracellular compartment of the basal keratinocytes to the underlying basement membrane, have been shown to be hypoplastic or rudimentary in different forms of JEB2. Previously, in different JEB phenotypes, mutations have been found in the three genes for the anchoring filament component laminin5 (LAMA3, LAMBS, and LAMC2)3–6 and in the gene for the hemidesmosome-associated integrin β4 subunit7. Here, we describe the first mutations in the gene encoding the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a transmembranous hemidesmosomal collagen, also known as type XVII collagen (COL17A1)8.The patient is affected with generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa (GABEB)9, a rare variant of JEB, and isacompound heterozygote for premature termination codons on both alleles. These novel findings emphasize the molecular heterogeneity of this group of genodermatoses, and attest to the importance of BPAG2 in maintaining adhesion between the epidermis and the dermis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fine, J.-D. et al. Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa. A consensus report by the Subcomittee on Diagnosis and Classification of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 24, 119–135 (1991).
Tidman, M.J. & Eady, R.A.J. Hemidesmosome heterogeneity in junctional epidermolysis bullosa revealed by morphometric analysis. J. invest. Dermatol. 86, 51–56 (1986).
Pulkkinen, L. et al. Mutations in the γ2 chain gene (LAMC2) of kalinin/ laminin-5 in the junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Nature Genet. 6, 293–298 (1994).
Aberdam, D. et al. Herlitz's junctional epidermolysis bullosa is linked to mutations in the gene (LAMC2) for the γ2 subunit of nicein/kalinin (laminin-5). Nature Genet. 6, 299–304 (1994).
Pulkkinen, L. et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the β3 chain gene of laminin 5 (LAMB3) in Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Genomics 24, 357–360 (1994).
Kivirikko, S. et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the mutation in the α3 chain gene of laminin 5 (LAMA3) in lethal (Herlitz) junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Hum. molec. Genet. 4, 959–962 (1995).
Vidal, F. et al. Mutations in the gene for the integrin β4 subunit are associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nature Genet. 10, 229–234 (1995).
Li, K., Tamai, K., Tan, E.M.L. & Uitto, J. Cloning of type XVII collagen. Complementary and genomic sequences of mouse 180-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2) predict an interrupted collagenous domain, a transmembranous segment, and unusual features in the 5′ end of the gene and the 3′-untranslated region of the mRNA. J. biol. Chem. 268, 8825–8834 (1993).
Hintner, H. & Wolff, K. Generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Arch. Dermatol. 118, 375 (1982).
Nishizawa, Y., Uematsu, J. & Owaribe, K. HD4, a 180 kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen, is a major transmembrane glycoprotein of the hemidesmosome. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 113, 493–501 (1993).
Owaribe, K., Nishizawa, Y. & Franke, W.W. Isolation and characterization of hemidesmosomes from bovine corneal epithelial cells. Expl. Cell Res. 192, 622–630 (1991).
Verrando, P. et al. Monoclonal antibody GB3 defines a widespread defect of several basement membranes and a keratinocyte dysfunction in patients with lethal junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Lab. Invest. 64, 85–92 (1991).
Giudice, G.J., Emery, D.J. & Diaz, L.A. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J. Invest. Dermatol. 99, 243–250 (1992).
Li, K. et al. Genomic organization of collagenous domains and chromosomal assignment of human 180 kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a novel collagen of stratified squamous epithelium. J. biol. Chem. 266, 24064–24069 (1991).
Keen, J., Lesler, D., Inglehorn, C., Curtis, A. & Bhattacharya, S. Rapid detection of single base mismatches as heteroduplexes on hydrolink gels. Trends Genet. 7, 5 (1991).
Urlaub, G., Mitchell, P.J., Ciudad, C.J. & Chasin, L.A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 2868–2880 (1989).
Cheng, J., Fogel-Petrovic, M. & Maquat, L.E. Translation to near the distal end of the penultimate exon is required for normal levels of spliced triosephosphate isomerase mRNA. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 5215–5225 (1990).
Uitto, J. & Christiano, A.M. Molecular genetics of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Perspectives on epidermolysis bullosa and other blistering skin diseases. J. clin. Invest. 90, 687–692 (1992).
Ishiko, A., Shimizu, H., Ebihara, T., Hashimoto, T. & Nishikawa, T. Human autoantibodies against the 230-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1) bind only to the intracellular domain of the hemidesmosome, whereas those against the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2) bind along the plasma membrane of the hemidesmosome in normal human and swine skin. J. clin. Invest 91, 1608–1615 (1993).
Burgeson, R.E. et al. A new nomenclature for laminins. Matrix Biol. 14, 209–211 (1994).
McGrath, J.A. et al. Altered laminin 5 expression due to mutations in the gene encoding the β3 chain (LAMB3) in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. J. invest. Dermatol. 104, 467–474 (1995).
Vailly, J. et al. Identification of a homozygous one-basepair deletion in exon 14 of the LAMB83 gene in a patient with Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa and prenatal diagnosis in a family at risk for recurrence. J. invest Dermatol. 104, 462–466 (1995).
Jonkman, M.F. et al. 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BP180) is deficient in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. J. clin. Invest. 95, 1345–1352 (1995).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning. a laboratory manual. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1989).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-termination inhibitors. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Sonnenberg, A. et al. A complex of platelet glycoproteins la and Ha identified by a rat monoclonal antibody. J. biol. Chem. 262, 10376–10383 (1987).
Jonkman, M.F., deJong, M.J.C.M., Heeres, K. & Sonnenberg, A. Expression of integrin a6(54 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. J. invest Dermatol. 99, 489–496 (1992).
Purkis, P.E. et al. Antibody markers of basal cells in complex epithelia. J. Cell Sci. 97, 39–50 (1990).
Leigh, I.M., Purkis, P.E. & Bruckner-Tuderman, L. LH7:2 monoclonal antibody detects type VH collagen in the sub-lamina densa zone of ectodermally-derived epithelia including skin. Epithelia 1, 17–29 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, J., Gatalica, B., Christiano, A. et al. Mutations in the 180–kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a hemidesmosomal transmembrane collagen (COL17A1), in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet 11, 83–86 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0995-83
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0995-83
This article is cited by
-
Collagen XVII deficiency alters epidermal patterning
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Identification of a Novel COL17A1 Compound Heterozygous Mutation in a Chinese Girl with Non-Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa
Current Medical Science (2020)
-
The direct binding of collagen XVII and collagen IV is disrupted by pemphigoid autoantibodies
Laboratory Investigation (2019)
-
The dysfunction of BP180/collagen XVII in keratinocytes promotes melanoma progression
Oncogene (2019)
-
Stem cell competition orchestrates skin homeostasis and ageing
Nature (2019)