Abstract
Objective: To examine interrelationships between (1) dietary habits, (2) socioeconomic and (3) environmental factors, and their impact on plasma retinol and plasma ascorbic acid.
Design: Cross-sectional study on adults from Western India.
Setting: Rural, semi urban, urban higher/middle/lower socioeconomic regions (HSE/MSE/LSE) having diverse dietary habits and environmental conditions.
Subjects: A total of 214 men and 108 women (20–50 y), apparently healthy and non-anemic.
Main outcome measures: Food intake by food frequency questionnaire, weight, height, age, smoking, environmental score, education, income, plasma retinol and plasma ascorbic acid.
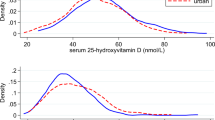
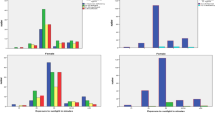
Results: Mean plasma retinol in women (24.84±5.1 µg/dl) and men (24.75±4.53 µg/dl) were not significantly different and 21% had plasma retinol below 20 µg/dl. Mean plasma ascorbic acid in women (0.35±0.12 mg/dl) and men (0.30±0.12 mg/dl) was similar with 75% having plasma ascorbic acid below 0.4 mg/dl. Vitamin A intake (as retinol equivalent) and plasma retinol showed a significant dose response (P<0.05) but not vitamin C intake and plasma ascorbic acid. Plasma retinol showed significant correlation with income (ρ=0.24), education (ρ=0.27), and environment (ρ=0.21; ρ=0.0001). Similar correlations with plasma ascorbic acid were 0.29, 031, −0.23 respectively (P=0.0001). Logistic regression showed education, environment, green leafy vegetables (GLV) and milk intake as predictors of plasma retinol deficiency, while non-sweet fruit intake, education and passive smoking for plasma ascorbic acid deficiency (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Subnormal status of retinol and vitamin C emphasizes the need to increase consumption of fruit, GLV and milk products, and also better education and environment. Avoiding passive smoking demands attention in order to improve levels of these vitamins.
Sponsorship: Department of Science and Technology, India (project no. SP/SO/B39/94).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu TK, Dickerson WP . 1996 Introduction. In Vitamins in Human Health and Disease 1–2 Wallingford, Oxon: CAB International
de Pee S, Bloem MW, Gorstein J, Sari M, Satoto Yip R, Shrimpton R, Muhilal . 1998 Reappraisal of the role of vegetables in vitamin A status of mothers in Central Java, Indonesia Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: 1068–1074
Drewnowski A, Rock CL, Henderson SA, Shore AB, Galan P, Preziosi P, Hercberg S . 1997 Serum β-carotene and vitamin C as biomarkers of vegetable and fruit intakes in a community-based sample of French adults Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65: 1796–1802
Gillman MW, Cupples LA, Gagnon S, Posner BM, Ellison RC, Castelli WP, Wolf PA . 1995 Protective effect of fruits and vegetables on development of stroke in men J.A.M.A. 273: 1113–1117
Gokhale MK, Chiplonkar SA, Sukhatme PV . 1993 Effect of environmental factors on growth and morbidity of urban Montessori children receiving supplementation Ecol. Food Nutr. 31: 269–276
Grusse J Le, Watier B . 1993 Les Vitamins Centre D-Etude et d'Information Surles Vitamines 48 France: Produits Roche
Hjartaker A, Lund E . 1998 Relationship between dietary habits, age, lifestyle and Se status among adult Norwegian women Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52: 565–572
Hulshof KFAM, Lowik MRH, Kok FJ, Wedel M, Brants HAM, Hermus RJJ, ten Hoor F . 1991 Dietary and other life style factors in high and low socioeconomic groups. (Dutch nutrition surveillance system) Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 45: 441–450
ICMR . 1990 Nutrient requirements and recommended dietary allowances for Indians. A report of the expert group of the Indian Council of Medical Research India 30, 78–99
Johanson L, Solvoll K, Bjarnchoe G-Eas, Drevon CA . 1997 Dietary habits among Norwegian men and women Scand. J. Nutr. 2: 63–70
Law MR, Morris JK . 1998 By how much does fruit and vegetable consumption reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52: 549–556
Matilainen T, Vartianen E, Puska P, Alfthan G, Pokusajeva S, Moisejeva N, Uhanov M . 1996 Plasma ascorbic acid concentration in the Republic of Korelia, Russia and North Korelia, Finland Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50: 115–120
NNMB . 1991 National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau Report of Repeat Surveys (1988–1990) Hyderabad: National Institute of Nutrition, ICMR
NSS . 1996 Key Results on Household Consumer Expenditure National Sample Survey Organisation Department of Statistics, Government of India Report no 401, 50th Round (July 1993–June 1994) 7–8
Ness AR, Powles JW . 1997 Fruit and vegetables and cardiovascular disease: a review Int. J. Epidemiol. 26: 1–13
Ness AR, Cappuccio FP, Atkinson RW, Khaw KT, Cook DG . 1999 Plasma vitamin C levels in men and women from different ethnic backgrounds living in England Int. J. Epidemiol. 28: 450–455
Olson JA . 1990 In Handbook of Vitamins, ed. LJ Machlin 1–57 New York: Marcel Dekker
Raghuramulu N, Madhavan Nair K, Kalayansundaram S . 1983 Manual of Laboratory Techniques 31–33, 121, 125 Hyderabad: National Institute of Nutrition
Sankhla A, Dashora PK, Sankhla AK . 1991 Vitamin A status of urban and rural adults of Agra district Ind. J. Nutr. Diet. 28: 224–227
Sauberlich HE, Machlin LG . 1992 Beyond deficiency: new views on the function and health effects of vitamins Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 669: 197–313
Sinha M, Sharma KK . 1998 Plasma antioxidant vitamin C and E in relation to coronary heart disease risk factors Ind. J. Nutr. Diet. 35: 204–210.
Smith AM, Baghurst KR . 1992 Public health implications of dietary differences between social status and occupational category groups J. Epidemiol. Community Health 46: 409–416
Spirichev VB, Blazheevich NB, Kodentsov VM, Isaeva XA, Sokol Nikov AA, Brzhesinskaya OA, Beketova NA, Kharitonchik LA, Alekseeva IA, Aleinik SI, Yakushina LM, Pereverzeva OG . 1995 Vitamin status of adult population of the Russian Federation and its changes in 1983–93. 1. Vitamins C and E and carotene Voprosy Pitaniya 4: 5–12
Steinmetz KA, Potter JD . 1996 Vegetables fruits and cancer prevention. A Review J. Am. Dietet. Assoc. 96: 1027–1039
Vijayalakshmi P, Rema SR . 1994 Biochemical profile of selected normal healthy adult men and women Ind. J. Nutr. & Diet 31: 277–284
Willett W . 1998 Nutritional Epidemiolog, 2nd ed. Press. New York: Oxford University.
Ziegler RG, Subar AF . 1991 Vegetables, fruits and carotenoids and the risk of cancer. In Micronutrients in Health and in Disease Prevention, ed. A Bendich & CE Butterworth 97–126 New York: Marcel Dekker
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India (Project no. SP/SO/B39/94).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiplonkar, S., Agte, V., Mengale, S. et al. Are lifestyle factors good predictors of retinol and vitamin C deficiency in apparently healthy adults?. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 96–104 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601291
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601291
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identifying risk factors in explaining women’s anaemia in limited resource areas: evidence from West Bengal of India and Bangladesh
BMC Public Health (2022)
-
Screening score for early detection of cardio-metabolic risk in Indian adults
International Journal of Public Health (2017)
-
Research Letters
Indian Pediatrics (2014)
-
Plasma vitamin C levels and risk of preterm prelabour rupture of membranes
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2011)
-
Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology: applications, needs and new horizons
Human Genetics (2009)